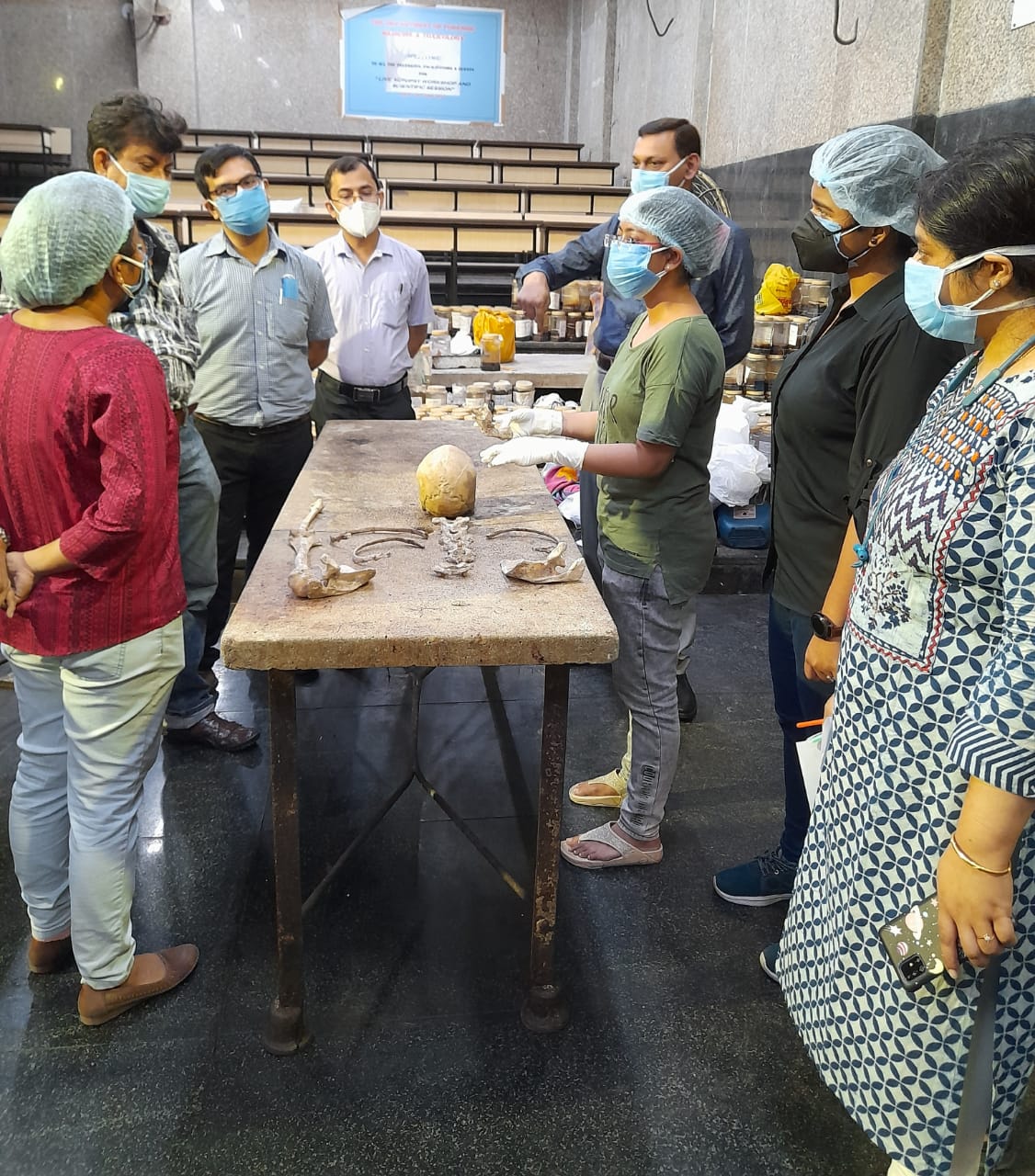
The Department of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology is involved in Udergraduate and Post graduate teaching along with providing Medicolegal Services. Since 1955 it has been actively functioning to provide Medicolegal Services to the State. Stalwarts like Professor JB Mukherjee and Professor CC Mallick have guided the department through all odds. The present Department is housed in a building inaugarated in 2015. The ground floor of the Department has a well equipped mortuary with provision for preservation of 48 dead bodies and a dissestion hall. The academic section of the department lies on the second and third floor with 4 demonstration rooms, departmental library cum seminar room and a museum. Research activities are conducted in the departmental Research laboratory on the first floor.
Apart from regular undergraduate and postgraduate teaching the department conducts examination of survivors and accused of sexual offence cases, medical examination for estimation of age and assessment of injury cases. The annual load of postmortem examination is approximately 3800. The dedicated faculty members, residents and the non teaching staff work tirelessly to uphold the esteem of the department.
UG Programs
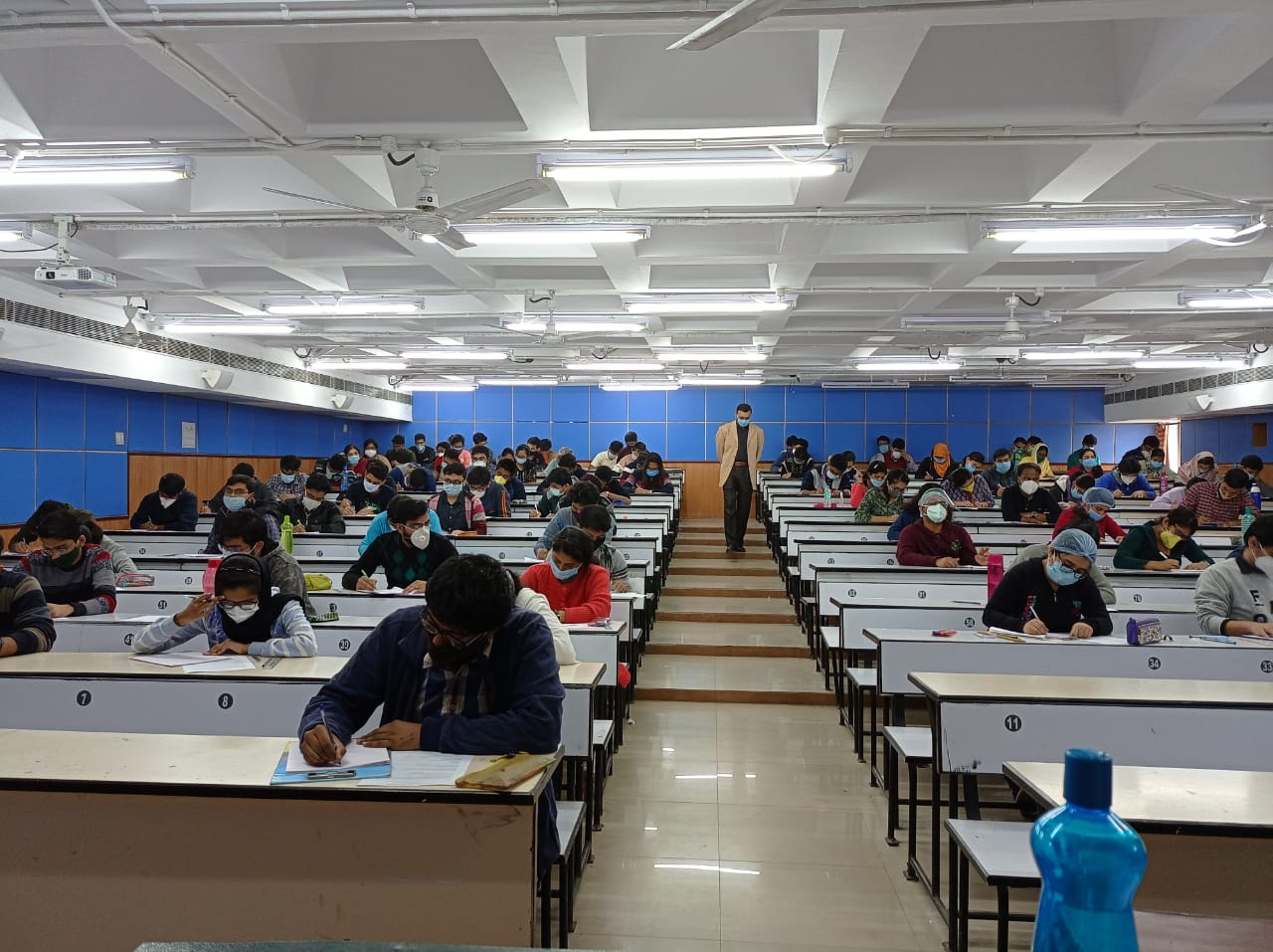
The National Medical Commission has revised the undergraduate medical education curriculum so that the Indian Medical Graduate (IMG) is able to recognize “Health for all” as a national goal. He/she should also be able to fulfill his/her societal obligations. The revised curriculum has specified the competencies that a student must attain and clearly defined teaching learning strategies for the same. With this goal in mind, early clinical exposure, foundation course, integrated teaching, skill development, AETCOM and self-directed learning have been introduced. There would be emphasis on communication skills, basic clinical skills and professionalism. There is a paradigm shift from the traditional didactic classroom-based teaching to learning environments where there is emphasis on learning by exploring, questioning, applying, discussing, analyzing, reflecting, collaborating and doing. The recognition of this need is enshrined by a greatly enhanced allocation of time to these methods and also the assessment techniques. With this view in mind the log book has been designed as per the guidelines of competency Based curriculum.
Professional teaching hours- Forensic Medicine & Toxicology
|
Teaching method |
Hours (II Phase + III-I Phase) |
|
Lectures |
15 + 25 |
|
SGD/Tutorial/Practical |
30 + 45 |
|
Self-Directed Learning (SDL) |
5 + 5 |
|
Total |
125 |
|
Phase - II MBBS |
Subjects |
Theory Marks |
PracticalMarks |
|
First Internal Assessment |
Forensic Medicine |
50 |
50 |
|
Phase - III/I MBBS |
Subjects |
Theory Marks |
PracticalMarks |
|
Second Internal Assessment |
Forensic Medicine |
50 |
50 |
|
Prelims |
Forensic Medicine |
100 |
100 |
|
University |
Forensic Medicine |
100 |
100 |
Certifiable skills
|
Sr. No. |
Competency No. |
Competency |
|
1 |
FM 14.20 |
To record and certify dying declaration in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
2 |
FM 14.22
|
To give expert medical /medico-legal evidence in Court of law.
|
|
3 |
FM 14.2 |
Demonstrate the correct technique of clinical examination in a suspected case of poisoning & prepare medico legal report in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
4 |
FM14.3 |
Assist and demonstrate the proper technique in collecting, preserving and dispatch of the exhibits in a suspected case of poisoning along with clinical examination.
|
|
5 |
FM8.9 |
Describe the procedure of intimation of suspicious cases or actual cases of foul play to the police, maintenance of records, preservation and dispatch of relevant samples for laboratory analysis.
|
|
6 |
FM14.6
|
Demonstrate and interpret medico legal aspects from examination of hair (Human & Animal), fiber, semen & other biological fluids.
|
|
7 |
FM 14.4 |
Conduct and prepare report of estimation of age of a person for medico legal and other purposes & prepare medico-legal report in a simulated/supervised environment
. |
|
Sr. No. |
Competency No. |
Competency |
|
8 |
FM 14.1
|
Examine and prepare Medico-legal report of an injured person with different etiologies in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
9 |
FM 14.11
|
To identify & describe weapons of medico legal importance which are commonly used. Able to prepare report of the weapons brought by police and to give opinion regarding injuries present on the person as described in injury report/ PM report so as to connect weapon with the injuries. (Prepared injury report/PM report must be provided to connect the weapon with the injuries)
|
|
10 |
FM14.12 |
Describe the contents and structure of bullet and cartridges used & to provide medico-legal interpretation from these.
|
|
11 |
FM 14.10
|
Demonstrate ability to identify & prepare medico legal inference from specimens obtained from various types of injuries e.g. contusion, abrasion, laceration, fire arm wounds, burns, head injury, and fracture of bone.
|
|
12 |
FM14.16 |
To examine & prepare medico legal report of drunk person in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
Sr. No. |
Competency No. |
Competency |
|
13 |
FM2.21 |
Mechanical Asphyxia: Describe and discuss different types of hanging and strangulation including clinical findings, causes of death, post mortem findings and medico legal aspects of death due to hanging and strangulation including examination, preservation and dispatch of ligature material.
|
|
14 |
FM 14.14
|
To examine & prepare report of an alleged accused in rape / unnatural sexual offence in a simulated / supervised environment.
|
|
15 |
FM 14.15
|
To examine & prepare report of a victim of rape/unnatural sexual offence in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
16 |
FM11.1 |
Describe features and management of Snake bite, scorpion sting, bee and wasp sting and spider bite.
|
|
17 |
FM14.17 |
To identify & draw medico legal inference from common poisons e.g. datura, castor, cannabis, opium, aconite, copper sulphate, pesticide compounds, marking nut, oleander, nux vomica,abrus seeds, snakes, capsicum, calotropis, lead compounds & tobacco.
|
|
18 |
FM 2.17 |
Describe and discuss exhumation.
|
|
19 |
FM 14.9
|
Demonstrate examination of bundle of bones & present an opinion after examination of skeletal remains in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
Sr. No. |
Competency No. |
Competency |
|
20 |
FM 1.9
|
Describe the importance of documentation in medical practice in regard to medico legal examination, medical certificates and medico legal reports especially - documents of issuance of sickness and fitness certificate.
|
|
21 |
FM 1.9 |
Describe the importance of documentation in medical practice in regard to medico legal examination, medical certificates and medico legal reports especially-maintenance of patient case records, discharge summary, prescribed registers to be maintained in Health centres - documents for issuance of death certificate documents of Medical certificate of Cause of Death – Form 4 & 4A.
|
|
22 |
FM1.10 |
Select appropriate cause of death in a particular scenario by referring ICD 10 code.
|
|
23 |
FM1.11 |
Write a correct cause of death certificate as per ICD 10 document.
|
|
24 |
FM14.7 |
Demonstrate & identify that a particular stain is blood and identify the species of its origin.
|
|
25 |
FM14.21
|
To collect, preserve, seal and dispatch exhibits for DNA-Finger printing using various formats of different laboratories.
|
|
26 |
FM 14.13
|
To estimate the age of fetus by post mortem examination.
|
|
27 |
FM 14.18
|
To examine & prepare medico legal report of a person in police, judicial custody or referred by Court of Law and violation of human rights as requirements of NHRC, who has been brought for medical examination.
|
|
28 |
FM 14.5
|
Conduct & prepare post-mortem examination report of varied etiologies (at least 15) in a simulated/supervised environment.
|
|
29 |
FM14.19 |
To identify & prepare medico legal inference from histo-pathological slides of Myocardial infarction, pneumonitis, tuberculosis, brain infarct, liver cirrhosis, brain haemorrhage, bone fracture, pulmonary oedema, brain oedema, soot particles, diatoms & wound healing.
|
PG Prog :
PG Programs
The purpose of PG education is to create specialists who would provide high quality health care and advance the cause of science through research & training. This programme is meant to standardize and strengthen Forensic Medicine teaching at the post graduate level throughout the country so that it will benefit the judiciary and the legal system of the country in providing justice which will ultimately benefit the community at large. It will also help in achieving uniformity in undergraduate teaching. The purpose of this document is to provide teachers and learners illustrative guidelines to achieve defined outcomes through learning and assessment. This document was prepared by various subject-content specialists. The Reconciliation Board of Academic Committee has attempted to render uniformity without compromise to purpose and content of the document. Compromise in purity of syntax has been made in order to preserve the purpose and content. This has necessitated retention of “domains of learning” under the heading “competencies”.
SUBJECT SPECIFIC LEARNING OBJECTIVES
The Goal of MD Forensic Medicine is to train a doctor to become a competent medico-legal expert, teacher and researcher in the subject who:
1. is aware of medico legal aspects in various settings
2. is aware of contemporary advances and developments in the field of Forensic Medicine.
3. has acquired the competencies pertaining to the subject of Forensic Medicine that are required to be practiced at all levels of health system.
4. is oriented to the principles of research methodology.
5. has acquired skills in educating and imparting training to medical, paramedical and allied professionals.
A post graduate student, upon successfully qualifying in the M.D (Forensic Medicine) examination, should be able to:
1. Become an expert in Forensic Medicine.
2. Identify and define medico-legal problems as they emerge in the community and work to resolve such problems by planning, implementing, evaluating and modulating Medico- legal services.
3. Undertake medico-legal responsibilities and discharge medico-legal duties in required settings.
4. Keep abreast with all recent developments and emerging trends in Forensic Medicine, Medical Ethics and the law.
5. Deal with general principles and practical problems related to forensic, clinical, emergency, environmental, medico-legal and occupational aspects of toxicology.
6. Deal with medico-legal aspects of Psychiatry, mental health and drug addiction.
7. Impart education in Forensic Medicine and Toxicology to under-graduate and post- graduate students with the help of modern teaching aids.
8. Assess the students’ knowledge and skills in the subject of Forensic Medicine.
9. Oriented to research methodology and conduct of research in the subject.
SUBJECT SPECIFIC COMPETENCIES
By the end of the course, the student should have acquired knowledge (cognitive domain), professionalism (affective domain) and skills (psychomotor domain) as given below:
A. Cognitive domain
1. Describe the legal and medico-legal system in India.
2. Acquire knowledge on the philosophy and guiding principles of Forensic Medicine course.
3. Describe the programme goals and objectives of the Forensic Medicine course.
4. Acquire knowledge on conduct of medico-legal autopsy independently with required physical assistance, prepare report and derive inferences.
5. Outline the principles and objectives of postmortem examination.
6. Describe the formalities and procedures of medico-legal autopsies in accordance with existing conventions and the law.
7. Identify the role of anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, microbiology, pathology, blood bank, psychiatry, radiology, forensic science laboratory as well as other disciplines of medical science to logically arrive at a conclusion in medico-legal autopsies and examination of medico-legal cases.
8. Describe the principles of the techniques used in toxicological laboratory namely TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography), GLC (Gas Liquid Chromatography), AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry), HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) and Breath Alcohol Analyzer.
9. Describe relevant legal/court procedures applicable to medico-legal/medical practice.
10. Describe the general forensic principles of ballistics, serology, analytical toxicology and photography. 11. Interpret, analyze and review medico-legal reports prepared by other medical officers at the time of need.
12. Describe role of DNA profile and its application in medico-legal practice.
13. Describe the law/s relating to poisons, drugs, cosmetics, narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances. 14. Describe the legal and ethical aspects of Forensic Procedures including Narco-analysis, Brain mapping and Polygraph etc.
15. Describe the medico-legal aspects of Psychiatry, addiction and mental health.
B. Affective domain
1. Should be able to function as a part of a team, develop an attitude of cooperation with colleagues, and interact with the clinician or other colleagues to provide the best possible opinion.
2. Should be able to follow ethical principles in dealings with patients, police personnel, relatives and other health personnel and to respect their rights.
3. Follow medical etiquettes in dealing with each other.
4. Develop communication skills to word reports and professional opinion as well as to interact with patients, relatives, peers and paramedical staff, and for effective teaching.
C. Psychomotor domain
At the end of the course, the student should acquire following skills and be able to:
1. Perform medico-legal autopsy independently with required physical assistance, prepare report and derive inferences.
2. Perform medico-legal examination of users of alcohol, drugs and poisons and prepare report.
3. Perform medico-legal examination in cases of sexual offences and prepare report.
4. Interpret histo-pathological, microbiological, radiological, chemical analysis, DNA profile and other investigative reports for medico-legal purposes.
5. Perform medico-legal examination of bones, clothing, wet specimens and weapons.
6. Depose as an expert witness in a court of Law on medico-legal matters.
7. Examine, identify, prepare reports and initiate management on medico-legal cases in emergency set up.
8. Identify and discharge all legal responsibilities in medico-legal matters.
9. Plan, organize and supervise medico-legal work in general/teaching/district hospitals and in any health care set up.
10. Collect, preserve and dispatch various samples and trace evidences to the concerned authorities in appropriate manner.
11. Help and Advise authorities on matters related to medical ethics and medico-legal issues.
12. Discharge duties in respect of forensic, clinical, emergency, environmental, medico-legal and occupational aspects of toxicology.
13. Plan, organize and manage toxicological laboratory services in any health care set up.
14. Provide information and consultation on all aspects of toxicology to professionals, industry, Government and the public at large.
15. Manage medico-legal responsibilities in mass disasters involving multiple deaths like fire, traffic accident, aircraft accident, rail accident and natural calamities.
16. Do interaction with allied departments by rendering services in advanced laboratory investigations and relevant expert opinion.
17. Participate in various workshops/seminars/journal clubs/demonstration in the allied departments, to acquire various skills for collaborative research.
PD Prog :Other Courses :
| # | Title | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Departmental Publications | Download/ View |
| 2. | Departmental Services | Download/ View |
| # | Image | Name | Registration No. | Position | Resident Type | Publications | Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Dr Saurabh Chattopadhyay | 2 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 2 |  |
Dr Molly Banerjee | 8 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 3 |  |
Dr Sanjay Bandyopadhyay | 8 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 4 |  |
Dr Sayak Sovan Dutta | 4 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 5 |  |
Dr. Sandip Mukhopadhyay | 4 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 6 |  |
Dr. Manideepa Barua | 8 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 7 |  |
Dr. Rohit Sarkar | 117 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 8 |  |
Dr. Deepmalya Sengupta | 3 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 9 |  |
Dr. Sheikh Nadeem | 118 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 10 |  |
Dr. Arijit Bari | 117 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 11 |  |
Dr. M Mukesh | 119 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 12 |  |
Dr. Suklal Mandi | 119 | Resident | Download/ View | Download/ View |
| # | Image | Name | Position | Resident Type | Publications | Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mr. Sanjay Sarkar | 122 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 2 | Mr Abhijit Roy | 18 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 3 | Mrs. Kamala Devi Mallick | 122 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 4 | Manick Mallick, Bikki Mallick, Banty Mallick, Sahil Mallick, Sammi Mallick, Raj | 50 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View | |
| 5 | Mr. Rajendra Mallick , Mr. Rakesh Santra | 120 | Not resident | Download/ View | Download/ View |